Local Government 101
Local Government 101
City of Lansing Charter
What is a city charter?
A city charter is the document that describes the governing system for the city. It is sort of like a constitution- but for the city, instead of the federal government.
The charter includes many details of Lansing city government, such as mayoral powers, the number of members of the council, how council members are elected, and much more.
You can see the Lansing city charter here
Why is there a charter revision commission?
In November 2023, Lansing voters approved a ballot question for a general charter revision
As a result, on May 7, 2024, Lansing voters will elect 9 members to a charter revision commission. There are 36 candidates on the ballot.
What will happen next?
Once a commission is elected, they will have two and a half years to consider changes to the Lansing City Charter. Proposed changes would go to Lansing voters for approval.
City of Lansing Budget
In order to provide public services, a city must both collect and spend money. The leaders of the city must establish and maintain safeguards or controls to ensure that the city’s assets are safe from loss, theft, and misuse. They also must keep good records of all their financial data and transactions. All these functions and more are managed by the city finance department. The main tool the city has to affect financial decisions and the scope of policymaking is through the city budget.
Budget Preparation
The mayor will work with the directors of each city department to set priorities for the budget. This may include the opportunity for public input through one of the city’s participatory budget nights. After assessing the needs of the different city departments, the mayor will submit their proposed budget to the city council no later than the fourth Monday in March of each year as specified in the city charter. Participatory Budget Nights Information
2. Budget Adoption
The city council will review the mayor’s proposed budget. There will be a public hearing on the budget as well where input from the public can be heard. In order to approve the budget, the council must pass a resolution. Then make any appropriations so that the city can make payments using the budgeted funds. By the third Monday in May of each year, the city council must have a budget adopted for the coming fiscal year. City of Lansing 2023 - 2024 Budget
Lansing Revenues
Lansing Expenses
3. Revenues & Expenses
The city finance department collects tax and other revenue as authorized. City departments then make payments and transactions that the council allowed in the budget. No department can spend more than what was approved in the budget unless the council elects to amend the budget. The following charts show where the city’s money comes from and where it is spent. In 2023, the city had $603 million in revenue and spent $401 million. Breakdown of Revenues and Expenditures
4. Accounting
The city finance department employs professionals to regularly monitor and reconcile the city’s financial accounts. This is often done by comparing financial transactions to various records kept by the city, such as a general ledger. The staff identify any discrepancies in this information and find the cause of the discrepancy so it can be resolved. All the financial records are then compiled and summarized into a document known as the financial statements.
5. Audit
The audit is the final check and verification of all the city’s financial activity. The city hires an independent auditor from outside the city government to review all their financial information and the various controls they have in place and then issue their opinion on it. This is then put into an audit document along with the financial statements. The audit can be used by anyone to quickly evaluate the city’s financial position. City of Lansing 2023 Audit
City of Lansing Government Organization
The mayor of Lansing is Andy Schor, he is our 52nd mayor of Lansing. Some of his main priorities when taking office were neighborhoods, economic development, infrastructure, economic development, and Lansing schools. What many do not know is that the Lansing government has many different departments that work together to provide public services and carry out policy in the city.
The Mayor’s Office
The mayor of Lansing is a strong mayor who as a chief executive holds the power of veto, and directs the administration, appointment and removal of department heads and agencies. The mayor is elected for a 4 year term and the office is non-partisan meaning no political party associated can determine the nominee on the ballot.
These are some key mayoral powers and responsibilities:
Enforcement and Implementation of City of Lansing programs, services and activities outlined in the city charter.
Responsible for submitting a budget to the city council for approval.
Appointment power to the various heads of departments, boards, and commissions in the city (with city council approval).
Oversee the various city departments in the city of Lansing.
City Clerk
The City Clerk of Lansing handles elections and voter registrations for all citizens. In addition, the clerk office prepares agendas and printed proceedings for the Lansing City Council. The city Clerk oversees the proper maintenance of records in the City, and serves as the recording secretary to the Board of Ethics. The city clerk administers all oaths required for municipal purposes by law and is an approved United States Passport Acceptance Facility.
Fire Department
The Lansing Fire Department has a Board of Fire Commissioners with eight members that represent all wards within the City of Lansing, including two at-large positions. The Fire Commissioners have a wide range of authority including department budget approval, citizen complaints and department policies.
City Council
The Lansing City Council is elected by the voters in the city. It functions as the legislative branch for the city government. Four members are elected at-large (citywide) and four are elected from wards. Ward council members are voted on by city residents who live in the 4 wards in the city of Lansing. The city council holds public meetings at city hall at 7 pm on Mondays (for meeting schedule click here).
City Council powers:
Adopting the city budget proposed by the mayor with any amendments or recommendations from city council as needed
Write ordinances (laws) and penalties for violating them as well as enact ordinances.
Can override a mayoral veto by a 3/4th vote of city council members.
The president of the city council will become temporary mayor if the current mayor is absent.
City Assessor
The City Assessor's Office is responsible for keeping inventory of all property in the City of Lansing and taxable values for all property.
Link: City Assessor | Lansing, MI - Official Website (lansingmi.gov)
Human Relations & Community Service
The Human Relations and Community Services Department handles homelessness, food insecurity, health care, affordable housing, infant mortality, youth prevention programs, and refugee resettlement.
Link: Human Relations & Community Services | Lansing, MI - Official Website (lansingmi.gov)
City Attorney
The City Attorney provides legal advice and represents main “client” - the City of Lansing”. The city attorney handles any cases of criminal prosecution, civil litigation, Freedom of Information Act inquiries, employment-related matters, administrative hearings, and real estate transactions for the City of Lansing. In addition they answer any legal questions to the city council, mayor's office and city departments.
Police Department
The City of Lansing Police Department handles crime and promotes public safety in the City.
Link: Police Department | Lansing, MI - Official Website (lansingmi.gov)
Lansing Parks & Rec
The Department of Parks and Recreation handles maintenance of the parks, golf and municipal cemeteries in the City of Lansing.
Link: Parks & Recreation | Lansing, MI - Official Website (lansingmi.gov)
Economic Development and Planning
The Department of Economic Development and Planning handles the development and safety of housing projects in the City of Lansing.
The Office of Building Safety certifies the safe occupancy of buildings by verifying construction compliance with state-regulated building, electrical, fire, mechanical, and plumbing codes.
The Office of Planning oversees development, implementation, and review of the city’s Master Plan. Planning functions include comprehensive planning, site plan review, flood plain review, zoning review, historic preservation, public infrastructure, and review of economic development projects.
The Parking Services Office encompasses the operation of the municipal fee-based parking system.
The Development Office Housing Assistance handles federal and state grants for housing in the City of Lansing.
The Code Enforcement Office handles the preservation and improvement of houses that are safe, decent, and sanitary. Residents can use the Housing Enforcement Portal for building permits, code enforcement information, certificates of enforcement (rental certification) and projects by owner's name, address and/or parcel number.
City Treasury & Tax Department
The City Treasury & Income Tax Department is responsible for the administration of the City’s property tax and income tax programs. The Treasury division bills and collects the real, personal property, and delinquent personal property taxes. The Income Tax division collects Income Tax for Lansing residents and non-residents that work in Lansing.
Link: Treasury & Income Tax Office | Lansing, MI - Official Website (lansingmi.gov)
Neighborhoods and Citizen Engagement
The Department of Neighborhoods and Citizen Engagement (DNCE)’s supports neighborhoods with community dialogues, trainings, and connecting organizations to resources. The DNCE also helps neighborhoods form organizations that can advocate for the changes they wish to see in their neighborhoods.
Link: https://www.lansingmi.gov/180/Neighborhoods-Arts-Citizen-Engagement
Lansing’s Diversity Equity and Inclusion Department:
This department is dedicated to ensuring that Lansing is a model for a diverse and inclusive municipality. Some responsibilities of this department is:
Develop ongoing diversity and inclusion plans.
Review any ordinances and amendments to see if there are any potential negative effects that many impact certain communities more than others
Advise Lansing on any issues that relate to diversity, equity, and inclusion in the Lansing community
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in Lansing
Diversity Equity Dashboard:
This is a dashboard created by Lansing DEI as a way to provide transparency and tell an exciting story about Lansing through the lens of diversity.
The dataset is a compromise of indicators such as race, income, race/income, language, education, and more.
This dataset particularly studies employees of Lansing and to ensure quality data they continually improve it and it’s voluntary so people can choose to participate in it or not.
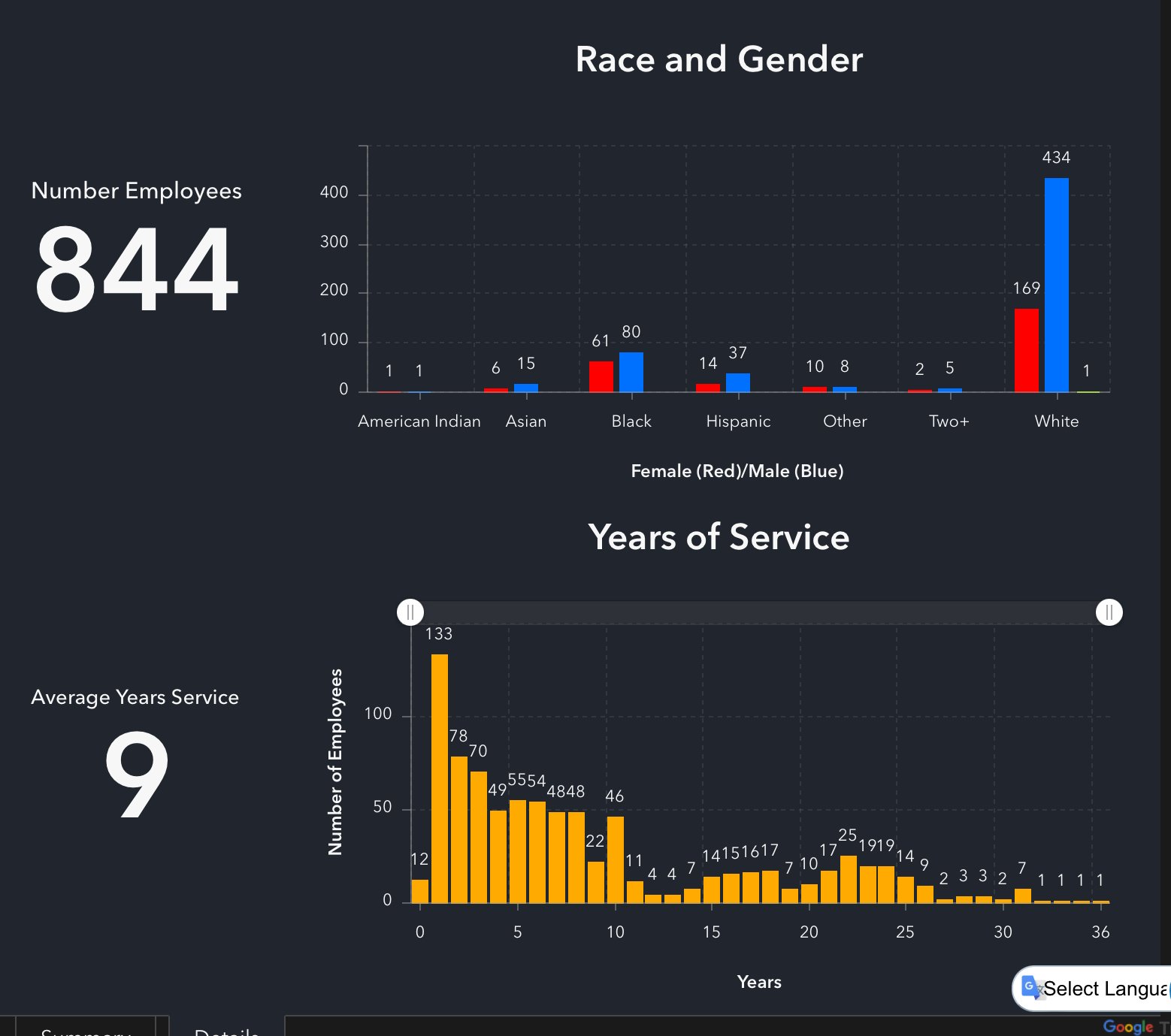
City of Lansing Workforce Diversity
Lansing Representation in State and Federal Governments
The people of Lansing are represented at the state and federal levels of government through elected officials.
Federal Level:
At the federal level, the people of Lansing have their interests and concerns represented through elected officials in the two houses of Congress: the Senate and House of Representatives.
US Senate
Each state in the United States has two Senators that represent the interests of the people of the state they represent.
Michigan’s two current senators are Debbie Stabenow and Gary Peters.
US House of Representatives
Each state has at least one member elected to the US House of Representatives. The number of elected officials in the US House of Representatives per state is based upon each state’s population.
For example, the state of California is going to have more elected officials than a state like Alaska because California has a much larger population than the state of Alaska.
Currently Michigan has 13 elected officials in the US House of Representatives.
Each elected official represents a specific district within Michigan made up of a handful of counties each.
The city of Lansing is represented by Representative Elissa Slotkin in US House District 7.
The people of Lansing can only vote for a house representative in District 7 .
State Level:
At the state level, the people of Lansing have their interests and concerns represented through elected officials in the two houses of the state legislature: the Senate and House of Representatives.
Michigan Senate:
There are 38 state senate districts in Michigan. Each district has a couple of counties within it. There is one elected official for each district, which means there are 38 senators in the Michigan Senate.
Michigan House of Representatives:
There are 110 state House of Representative districts in Michigan. Each district has one or more counties within it. There is one elected official for each district, which means there are 110 representatives.
One function of the state and federal government is to provide economic support for specific projects to local government units.
Crisis: Federal Response
In times of crisis, the state and federal government often provide assistance to local units of government until they can get back on their feet.
The most recent and well known incident of federal aid was in response to the Covid-19 Pandemic. Local units of government all over the US were overwhelmed by the expenses caused by the pandemic.
In response, the government provided economic support for several months. In Lansing specifically, the federal government provided around $49 million in economic aid to be used for things like providing revenue to support “essential workers”.
There are a number of ways in which the state and federal government aid can impact local units of government. The two examples mentioned above are only a small part of the complex yet essential relationship the state government and federal government have with the city of Lansing.
Service calls for city government?
Call 311
Residents of Lansing can call 311 as a one stop shop for any nonemergency questions related to the City of Lansing. Callers can report an issue and agents are able to directly create Service Requests for City workers to follow up on. Further implementation of text and email for residents to use and communicate with 311 personnel is planned.